Briefly Describe the Structure of Smooth Muscle
The structure of the small intestine is a long tube that is composed of smooth muscle that helps to move food through the GI tract. Smooth muscles comprise single tapering single nucleated cells.

Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle And Smooth Muscle Characteristics And Differences Youtube
The membrane surrounding the muscle fibers is called sarcolemma.

. Smooth muscle fibers are tapered at each end have a single nucleus and lack the striations of skeletal or cardiac muscle. It controls the movement of an organism. In addition the small intestine is lined with.
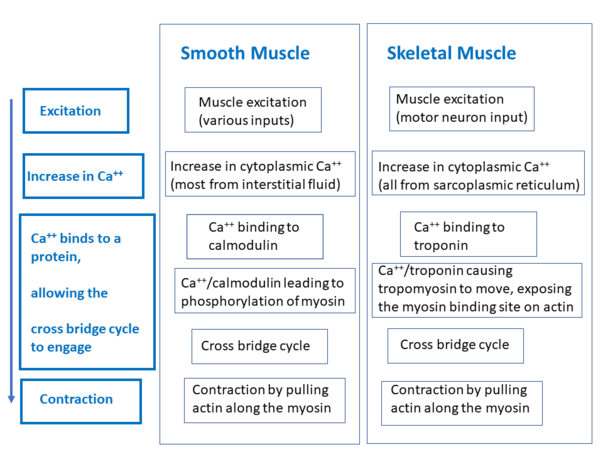
1993 Briefly discuss the role of calcium in the coupling of electrical and mechanical events in skeletal muscle. It is made up of thin and elongated cells called muscle fibers. It contains a network of membrane called the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
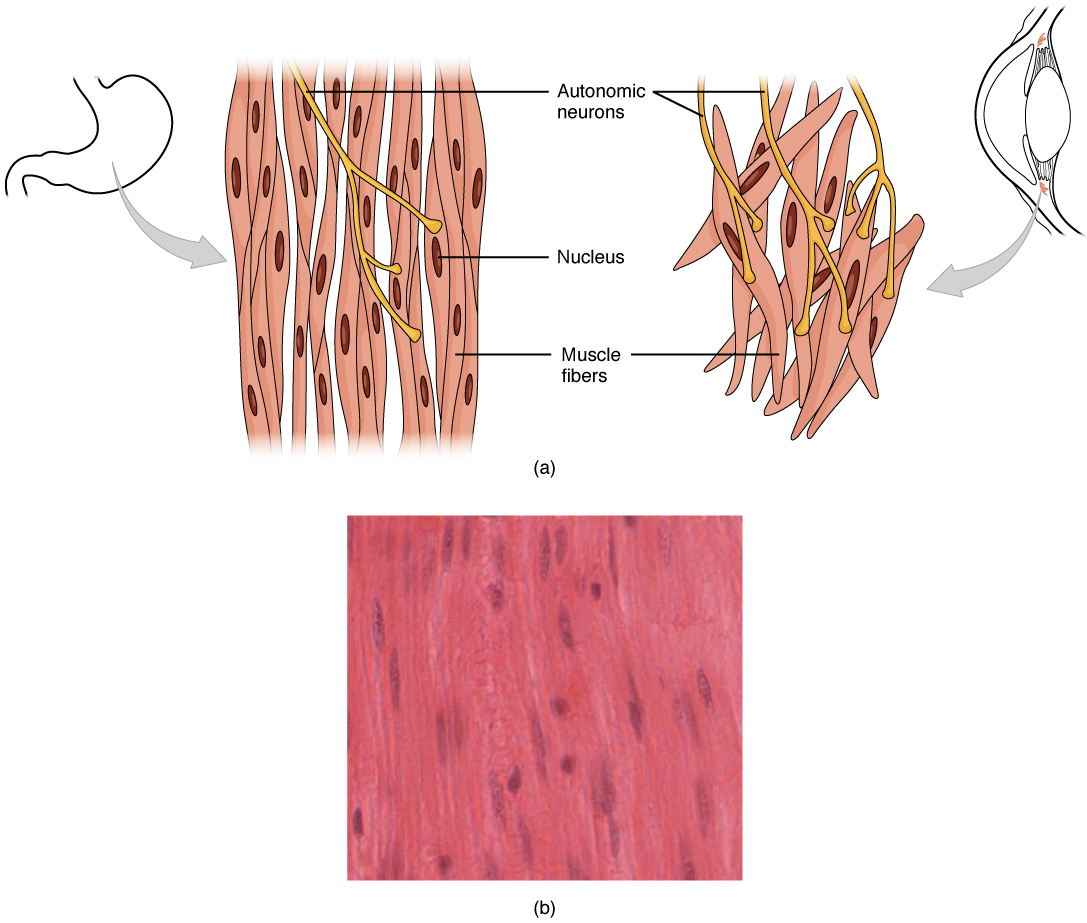
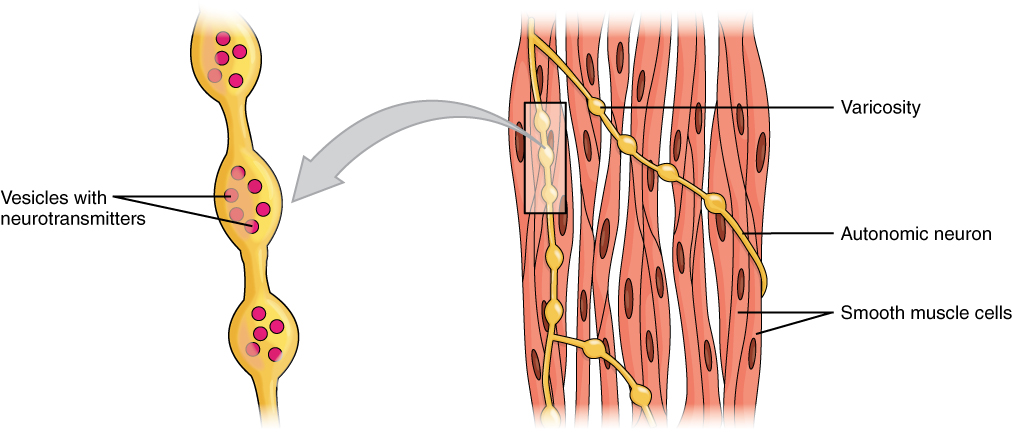
Each muscle comprises multiple tissues including blood vessels lymphatics contractile muscle fibers and connective tissue sheaths. A smooth muscle is composed of cells that are narrow and spindle-shaped with a single nucleus that is located centrally. A motor nerve ending also termed the presynaptic part.
Ii Each fibre is long unbranched and enclosed in a membrane called sarcolemma and its cytoplasm called sarcoplasm. Compare and contrast skeletal cardiac and smooth muscle tissue. The cytoplasm in the muscle fibers is called sarcoplasm.
For this reason unitary smooth muscle is often re-ferred to as visceral smooth muscle. A Write about structure and function of smooth muscle fibres. Physiological Anatomy of Neuromuscular Junction.
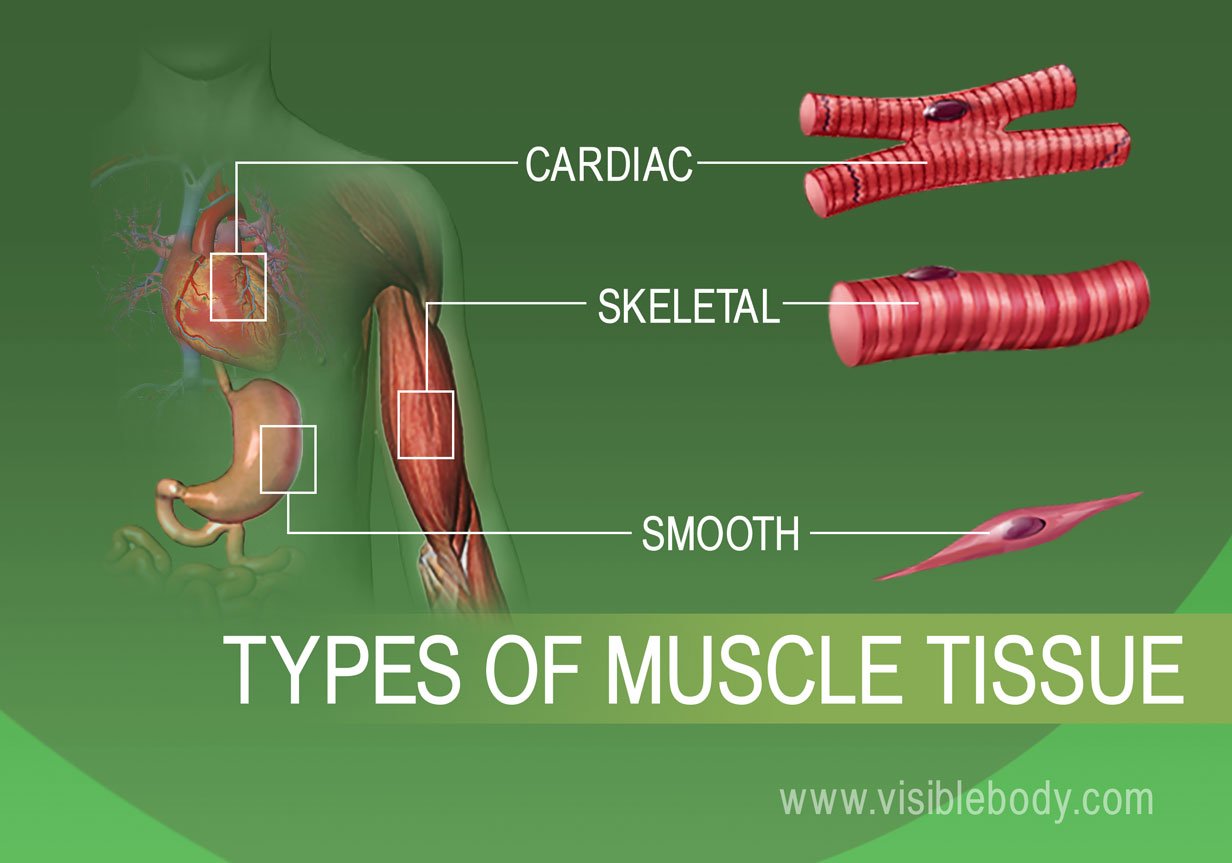
The cardiac muscle controls blood flow in the heart while the smooth muscles move food and other substances along the gastrointestinal system. Also Physiol-98B07 Physiol-12A12 Describe the main mechanisms by which chemical neurotransmitters exert their effects using examples. Describe the microscopic structure of a.
B Briefly describe cardiac muscle fibres. Of the three. An area between the.
Cardiac muscle cells are striated with many myofibrils in orderly arrangements. Briefly describe the structure and functions of the respiratory system. The structure of NMJ of a skeletal smooth or cardiac muscle vary a little from each other but all have three main parts.
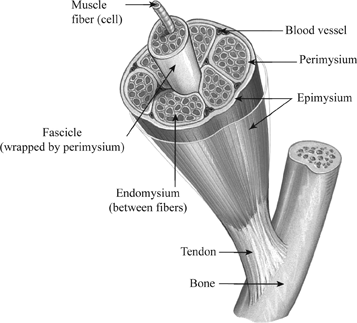
A globular head with a short arm - It is called the heavy meromyosin HMM. Outline the metabolic processes that occur in mitochondria. Each muscle is made up of groups of muscle fibers called fascicles surrounded by a connective tissue layer called perimysium.
Describe the mechanism underlying the knee jerk reflex. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia mitotically dividing to produce new cells. Smooth muscle is called unitary smooth muscle Fig.
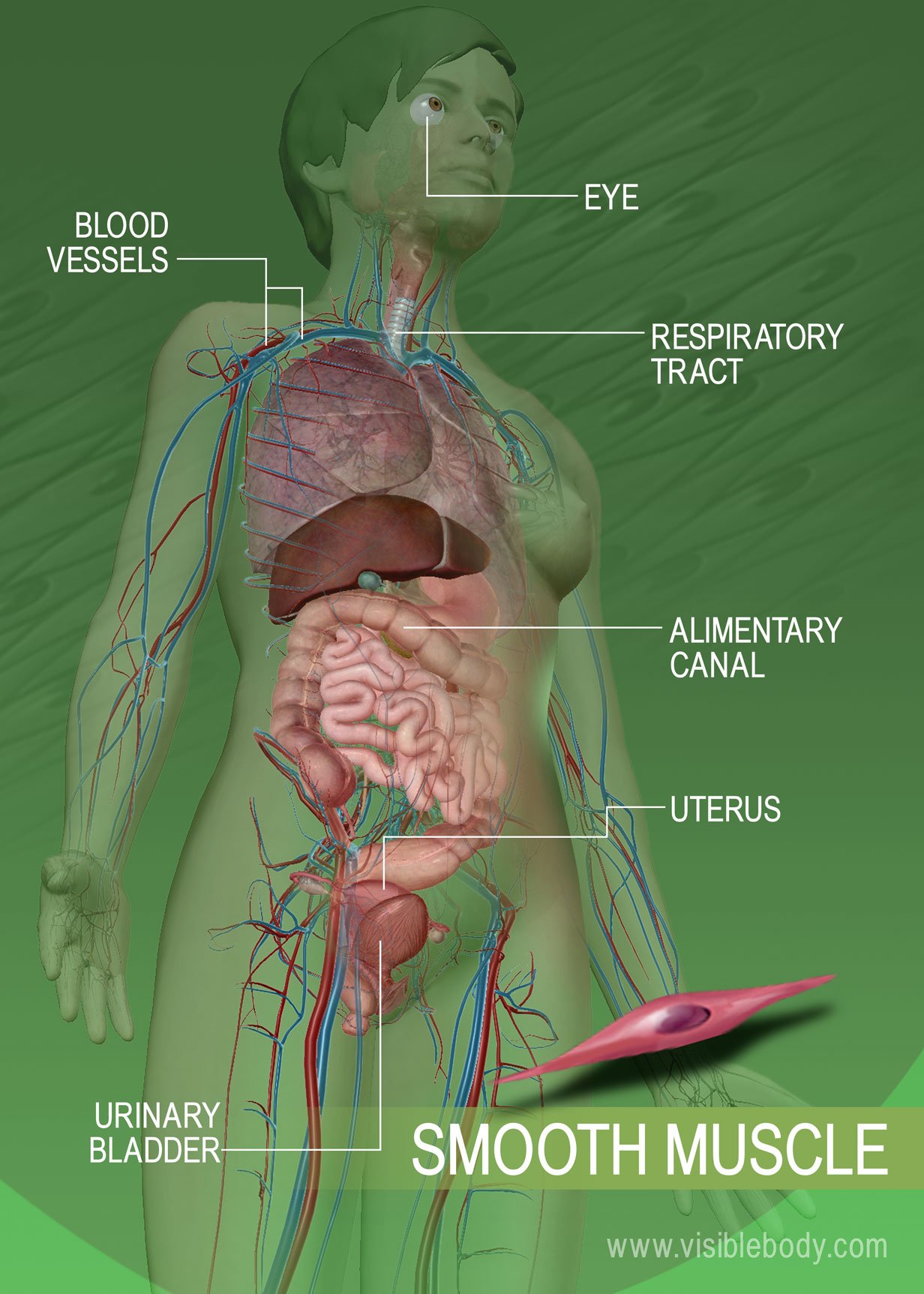
Smooth muscle which are situated in the walls of the hollow internal organs for example blood vessels the gastrointestinal tract bladder and uterus is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Iii The sarcoplasm contains many myofibrils that are long. The skeletal muscles are responsible for movements of the skeleton such as walking and moving arms.
Another group of muscles found within the muscular system are the smooth muscles. When viewed under a microscope they have a smooth even appearance. Smooth muscle lines the inside of blood vessels and organs such as the stomach and is also known as visceral muscle.
Also Physiol-11B09 Physiol-13A14 Briefly describe structure of mitochondria. T he head and short arm projects outwards at regular distance and angle from each other from the surface of a polymerised myosin filament and is known as cross arm. Name the layers of connective tissue that occur in and around a skeletal muscle and briefly describe a muscles blood and nerve supply.
Physiol-16A14 Describe the physiological role of prostaglandins on smooth muscle throughout the body. Smooth muscle has different functions in the Human body including. The thick are comprised of myosin and the thin are comprised of actin troponin and tropomyosin.
Smooth muscle contracts under. They also control facial tissues responsible for activities such as smiling or frowning. List four functional properties that distinguish muscle tissue from other tissues.
Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. The outermost sheath of connective tissue covering each muscle is called epimysium. I A voluntary muscle is a bundle of numerous striated muscle fibre.
Just beneath the sarcolemma in each fibre many nuclei occur thus these fibres are multi-nucleated. It is the weakest type of muscle but has an essential role in moving food along the digestive tract and maintaining blood circulation through the blood vessels. List the digestive organs in order from mouth to.
1990 Write short notes on isometric and isotonic muscle contraction. Unitary smooth muscle is the predominant smooth muscle type within the walls of visceral organs such as the gastrointestinal tract the uterus and many blood ves-sels. Smooth muscle cells are not striated.
Smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and are spindle-shaped. Postsynaptic part the motor endplate which is a part of the muscle membrane. As the name suggests these muscles are not striated but have a smooth appearance instead.
Meromyosin is made up of two parts. Smooth muscle is found in the wall of hollow organs passageways tracts eye and skin. Fibers of smooth muscle group in branching bundles which allows for cells to contract much stronger than those of striated musculature.
Myofilaments comprised of thick and thin filaments. Like all other cells the striated muscle fiber also has a cell membrane called sarcolemma a smooth endoplasmic reticulum called sarcoplasmic reticulum cytoplasm called sarcoplasm and cytoskeletal proteins which are of 3 types. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins.
Physiol-XXXX Describe the structure innervation and function of muscle spindles. They are considered involuntary because a person does not have to think about moving them in order for them to do their jobs. Briefly describe the structure of smooth muscle.
The cells of smooth muscles are made up of fibres of myosin and actin that run through the cells and are backed by a framework of various proteins wherein the filaments are arranged in a stacked pattern across the cell. But fewer myofibrils are. Myofibrils long thin cylindrical rods usually 1-2 µm in diameter that run within and parallel to the long axis of the muscle fiber.
Smooth muscle is found throughout the body around various organs and tracts. Briefly describe the structure of meromyosin. Skeletal muscle cells are striated with orderly arranged myofibrils.

Draw A Labelled Diagram Of Various Types Of Muscles Found In The Human Body
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1951/hAji9x7UR1SrWXVI9xqW3A_histology-smooth-muscle_english.png)
Smooth Muscle Structure Function Location Kenhub

A Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Vmsc Phenotypic Switching Under Download Scientific Diagram

Smooth Muscle Anatomy Britannica

Cellular Physiology Of Skeletal Cardiac And Smooth Muscle Physiology Of Cells And Molecules Medical Physiology 2e Updated Edition With Student Consult Online Access 2e Medical Physiology Boron 2nd Ed
Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology

Smooth Muscle Anatomy Britannica

10 7 Smooth Muscle Tissue Anatomy Physiology

Pdf Mechanism Of Smooth Muscle Contraction

A Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Vmsc Phenotypic Switching Under Download Scientific Diagram

Define Muscular Tissue Classify And Explain Different Types Of Muscles With The Help Of Suitable Diagrams Science Shaalaa Com
Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology
Muscle Tissue Types Learn Muscular Anatomy
Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology
Definition Of Microscopic Structure Of Muscle Chegg Com

Smooth Muscle Anatomy Britannica

Comments
Post a Comment